Migraine is a common neurological disorder that affects millions of people of all ages, nationalities and sexes. Like any other disease, their presence is manifested by symptoms experienced by patients and their existence allows physicians to diagnose.

The most common symptoms of migraine and famous and is the headache. Even if it does not, in the rarer forms of the disease, there is a clear sign of migraine. The headache that accompanies a migraine is not such a dull ache there. Pain that is intense migraine patients, throbbing type, which sometimes requires a complete rest and interferes with the normal functions of daily living.
However, a headache is not the only indicator that signals a migraine. According to the migraine attack, resulting in a variety of other symptoms. Analyze the doctor helps to determine what type of migraine, the patient and the prescription of appropriate drugs.
A survey of migraine symptoms may be long enough for the different types of diseases.
A general list of these include: severe headaches on one or both sides of the head, nausea, vomiting, weakness, visual disturbances, blurred vision and sensitivity to light, noise, pain above eyes, has the vision, and temporary blind spots. even though migraine with aura, which involves a new set of symptoms, which consists of: see lines flashing lights or zigzag, temporary blindness, speech difficulties, tingling and weakness in the limbs and face, confusion, dizziness and sensitivity to noise.
This does not mean the victim experiences any symptoms during the attack. Most likely, he will learn a few. Symptoms vary from person to person. It could also one day feel migraine symptoms before the attack, during the prodromal stage. In these times, feelings of joy or migraine inexplicable energy intense cravings for sweets, thirst, fatigue, irritability and depression.
diagnose migraine is not an easy task for the physician. To make an accurate assessment, it will be necessary to have as much information as possible to get it done by the patient and medical tests. The observation and analysis of symptoms is very helpful in arriving at a diagnosis. By knowing what symptoms are experienced by the patient, the specialist will be able to tell what type of migraine is and what treatments are administered. During the consultation, the patient is required to describe the duration and frequency of severe headaches and how they are, where the pain is, the presence of symptoms and behaviors during the headache. Because other diseases also sings like a migraine, they are excluded. One example is the fact that people are breaking with sinusitis also experience double vision and vision loss.
migraines, but light is not a pleasant event. But the victim can for a good cause by taking the attention and it crosses. The complexity of migraine and the difficulty of diagnosis, this means that no detail is insignificant. Thus, if the patient takes an active role in the treatment of his illness, it takes all symptoms of migraine unique.
How are migraines diagnosed?
To make a diagnosis, your health care provider will
- Take your medical history
- Ask about your symptoms
- Do a physical and neurological exam
An important part of diagnosing migraines is to rule out other medical conditions which could be causing the symptoms. So you may also have blood tests, an MRI or CT scan, or other tests.
How are migraines treated?
There is no cure for migraines. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing additional attacks.
There are different types of medicines to relieve symptoms. They include triptan drugs, ergotamine drugs, and pain relievers. The sooner you take the medicine, the more effective it is.
There are also other things you can do to feel better:
- Resting with your eyes closed in a quiet, darkened room
- Placing a cool cloth or ice pack on your forehead
- Drinking fluids
There are some lifestyle changes you can make to prevent migraines:
- Stress management strategies, such as exercise, relaxation techniques, and biofeedback, may reduce the number and severity of migraines. Biofeedback uses electronic devices to teach you to control certain body functions, such as your heartbeat, blood pressure, and muscle tension.
- Make a log of what seems to trigger your migraines. You can learn what you need to avoid, such as certain foods and medicines. It also help you figure out what you should do, such as establishing a consistent sleep schedule and eating regular meals.
- Hormone therapy may help some women whose migraines seem to be linked to their menstrual cycle
- If you have obesity, losing weight may also be helpful
If you have frequent or severe migraines, you may need to take medicines to prevent further attacks. Talk with your health care provider about which drug would be right for you.
Certain natural treatments, such as riboflavin (vitamin B2) and coenzyme Q10, may help prevent migraines. If your magnesium level is low, you can try taking magnesium. There is also an herb, butterbur, which some people take to prevent migraines. But butterbur may not be safe for long-term use. Always check with your health care provider before taking any supplements.
What are the ingredients in Fioricet?
The active ingredients in Fioricet are acetaminophen, caffeine, and butalbital.
How does Fioricet work?
The acetaminophen in Fioricet is a pain reliever, the caffeine works as a stimulant to increase the acetaminophen’s effectiveness, and the butalbital is a sedative that decreases anxiety while causing relaxation and sleepiness. These actions are believed to ease migraine symptoms, but there is limited evidence that barbituates ease migraine symptoms.1
What are the possible side effects of Fioricet?
The most common side effects from Fioricet include:
-
-
- Drowsiness
- Upset stomach
- Vomiting
- Stomach pain
- Depression
- Lightheadedness
- Confusion
-
The following side effects could be signs of allergy or more serious complications and should be reported to health provider immediately:
-
- Skin rash
- Itching
- Difficulty breathing
This is not an exhaustive list of all potential side effects of Fioricet. For more information, consult your doctor or healthcare provider. Patients should talk to their doctor about what to expect with treatment with Fioricet. If you notice any new or worsening side effects, contact your doctor or healthcare provider immediately.
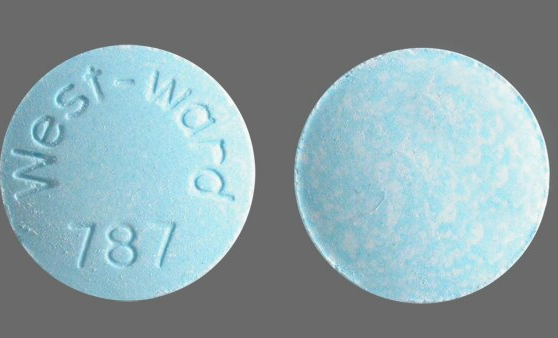
Major Pharmaceuticals Inc, a Harvard Drug Group Company
Pill Identification: West-ward 787
Item 13 of 23
Drug Image file DrugItem_18680.JPG
Things to note about Fioricet
Fioricet can be habit-forming, so you should use extreme caution if you decide to take it. Additionally, some people who take barbituates or opioids for extended periods can experience rebound headaches, which can increase in severity. These are also known as MOH, or medication overuse headaches.1
Barbituates can cause drowsiness, and their effect can be increased by alcohol use. It is important not to drive or use heavy machinery until you know how this drug affects you.2
Before taking Fioricet, tell your doctor if you:
- Are allergic to any ingredients in the medication
- Are taking blood thinners, antidepressants, antihistamines, or other sedatives like sleeping pills or tranquilizers.
- Are taking pain medications. Many over-the-counter pain relievers contain acetaminophen, and too much of this drug can be harmful.
- Have ever had liver disease, porphyria, or depression
- Are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or are breastfeeding2
You should begin no medication or supplement without first checking with your health care provider and should let them know of any other prescriptions, OTCs, and herbals you are taking to ensure there are no interactions.